
We are now linking our new container to the already launched MongoDB server container. Sudo docker run –it –link=tender_poitras:mongo mongo /bin/bash Let’s issue the following command for this − Step 5 − Now let’s spin up another container which will act as our client which will be used to connect to the MongoDB database. It is listening on the TCP port of 27017.
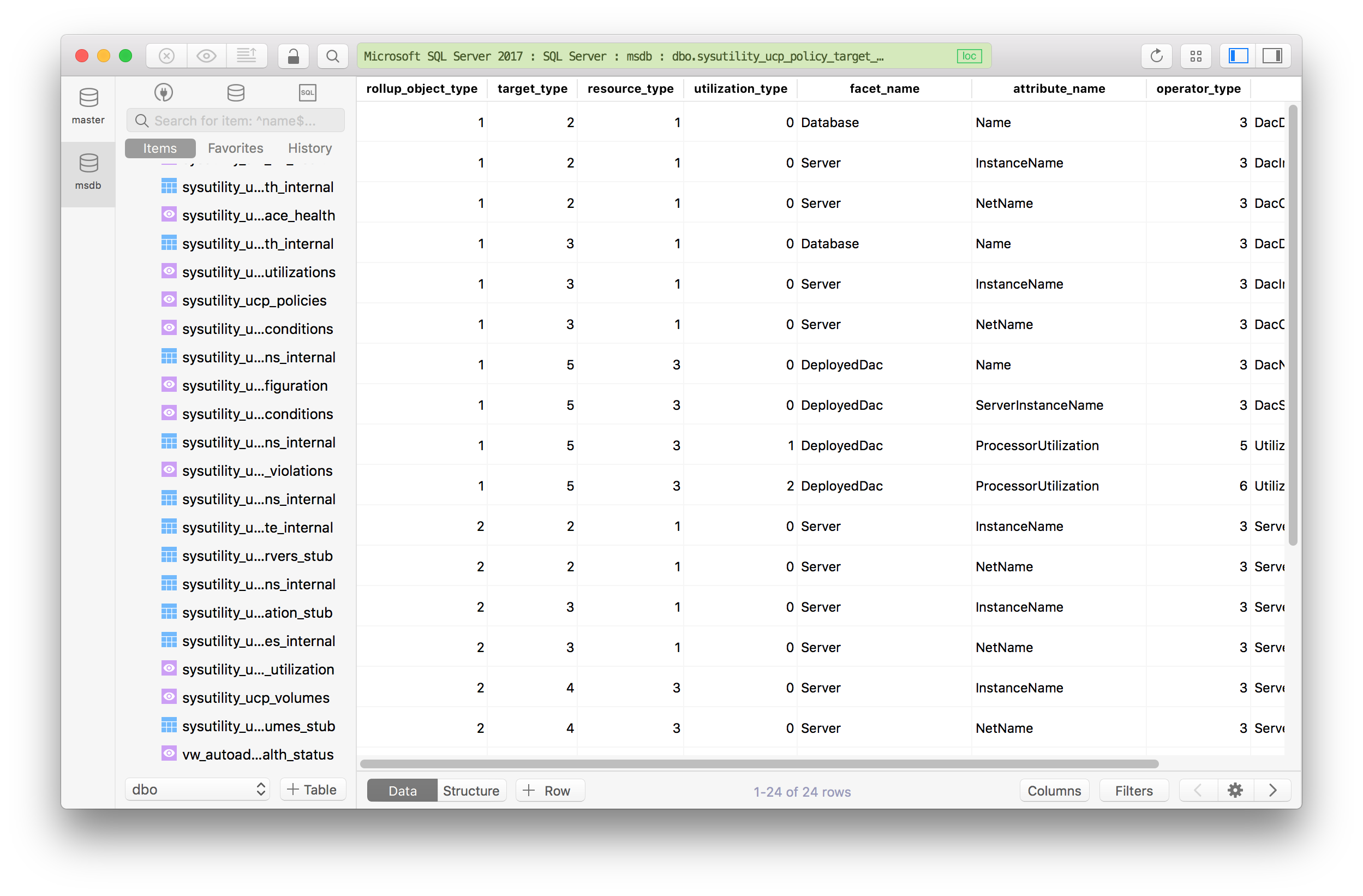
Next, also notice the port number it is running on. But just make a note of the container which you have launched. This name will be different since the name of the containers keep on changing when you spin up a container. The name of the container is tender_poitras. You can then issue the docker ps command to see the running containers −
The –d option is used to run the container as a daemon process.Īnd finally we are creating a container from the Mongo image.

The –it option is used to run the container in interactive mode. The following points can be noted about the above command − For this, we will issue the following command − Step 4 − Now that we have the image for Mongo, let’s first run a MongoDB container which will be our instance for MongoDB. Step 3 − On the Docker Host, use the Docker pull command as shown above to download the latest Mongo image from Docker Hub. Step 2 − You will see that the Docker pull command for Mongo in the details of the repository in Docker Hub. Just type in Mongo in the search box and click on the Mongo (official) link which comes up in the search results. When you log into Docker Hub, you will be able to search and see the image for Mongo as shown below. Step 1 − The first step is to pull the image from Docker Hub. We will now see the various steps for getting the Docker container for MongoDB up and running. Since MongoDB is a popular database for development, Docker has also ensured it has support for MongoDB. MongoDB is a famous document-oriented database that is used by many modern-day web applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
